Dynamic Algorithm to Compute the Longest Common Subsequence
- 时间:2020-10-11 15:25:20
- 分类:网络文摘
- 阅读:126 次
Given two strings text1 and text2, return the length of their longest common subsequence.
A subsequence of a string is a new string generated from the original string with some characters(can be none) deleted without changing the relative order of the remaining characters. (eg, “ace” is a subsequence of “abcde” while “aec” is not). A common subsequence of two strings is a subsequence that is common to both strings.
If there is no common subsequence, return 0.
Example 1:
Input: text1 = “abcde”, text2 = “ace”
Output: 3
Explanation: The longest common subsequence is “ace” and its length is 3.Example 2:
Input: text1 = “abc”, text2 = “abc”
Output: 3
Explanation: The longest common subsequence is “abc” and its length is 3.Example 3:
Input: text1 = “abc”, text2 = “def”
Output: 0
Explanation: There is no such common subsequence, so the result is 0.Constraints:
1 <= text1.length <= 1000
1 <= text2.length <= 1000
The input strings consist of lowercase English characters only.Hints:
Try dynamic programming. DP[i][j] represents the longest common subsequence of text1[0 … i] & text2[0 … j].
DP[i][j] = DP[i – 1][j – 1] + 1 , if text1[i] == text2[j] DP[i][j] = max(DP[i – 1][j], DP[i][j – 1]) , otherwise
Longest Common Subsequence using Dynamic Programming Algorithm
Sure, we can bruteforce, try to find all the common subsequence from both strings, and compare if they match. But the complexity is so high that it won’t be practical.
One better solution is to use the dynamic programming algorithm where we use a two dimensional array dp[i][j] to store the maximum length of the common subsequence from s1[0..i] and s2[0..j].
Then, a O(N^2) qudaric loop is needed, if we have s1[i] == s2[j], we update the answer to dp[i-1][j-1], otherwise, it is the maximum of dp[i-1][j] and dp[i][j-1].
The DP formula is:
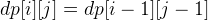 if
if 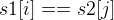
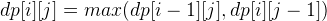 if
if 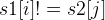
By implementing the above equations, we have the following C++ code.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | class Solution { public: int longestCommonSubsequence(string text1, string text2) { int len1 = text1.size(); int len2 = text2.size(); vector<vector<int>> dp(len1, vector<int>(len2, 0)); dp[0][0] = text1[0] == text2[0] ? 1 : 0; for (int i = 0; i < len1; ++ i) { for (int j = 0; j < len2; ++ j) { if (text1[i] == text2[j]) { if ((i > 0) && (j > 0)) { dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1; } else { dp[i][j] = 1; } } else { if (i > 0) dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j], dp[i - 1][j]); if (j > 0) dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j], dp[i][j - 1]); } } } return dp.back().back(); } }; |
class Solution {
public:
int longestCommonSubsequence(string text1, string text2) {
int len1 = text1.size();
int len2 = text2.size();
vector<vector<int>> dp(len1, vector<int>(len2, 0));
dp[0][0] = text1[0] == text2[0] ? 1 : 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len1; ++ i) {
for (int j = 0; j < len2; ++ j) {
if (text1[i] == text2[j]) {
if ((i > 0) && (j > 0)) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = 1;
}
} else {
if (i > 0) dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j], dp[i - 1][j]);
if (j > 0) dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
}
}
}
return dp.back().back();
}
};If we slightly increase the DP array by one, and update dp[i+1][j+1], we have a cleaner code.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | class Solution { public: int longestCommonSubsequence(string text1, string text2) { int n1 = text1.size(), n2 = text2.size(); vector<vector<int>> dp(n1 + 1, vector<int>(n2 + 1)); for (int i = 0; i < n1; ++ i) { for (int j = 0; j < n2; ++ j) { if (text1[i] == text2[j]) { dp[i + 1][j + 1] = dp[i][j] + 1; } else { dp[i + 1][j + 1] = max(dp[i + 1][j], dp[i][j + 1]); } } } return dp[n1][n2]; } }; |
class Solution {
public:
int longestCommonSubsequence(string text1, string text2) {
int n1 = text1.size(), n2 = text2.size();
vector<vector<int>> dp(n1 + 1, vector<int>(n2 + 1));
for (int i = 0; i < n1; ++ i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n2; ++ j) {
if (text1[i] == text2[j]) {
dp[i + 1][j + 1] = dp[i][j] + 1;
} else {
dp[i + 1][j + 1] = max(dp[i + 1][j], dp[i][j + 1]);
}
}
}
return dp[n1][n2];
}
};Both implementations are having O(N^2) time and space complexity.
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
推荐阅读:0有哪些含义 这口井有几米深? 拿破仑三角形 求甲乙两车的速度 获纪念奖的有多少人? 程大位与剩余定理 “位数”和“数位”的意义为什么不同? 节约用水的资料 求发芽率、合格率、出粉率等百分率的公式中为什么都要乘100%? 为什么公历7月和8月都是31天
- 评论列表
-
- 添加评论