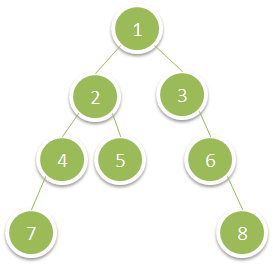
Compute the Deepest Leaves Sum of a Binary Tree using BFS or DFS
- 时间:2020-09-12 10:17:13
- 分类:网络文摘
- 阅读:110 次
Given a binary tree, return the sum of values of its deepest leaves.
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,6,7,null,null,null,null,8]
Output: 15
binary-tree
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is between 1 and 10^4.
The value of nodes is between 1 and 100.
We can traversal the binary tree using level-by-level namely Breadth First Search algorithm or depth first search.
Breadth First Search Algorithm to Compute the Deepest Leaves Sum of a Binary Tree
We can expand all the nodes in the same level by sum up on those. However, we need to reset the sum to zero when expanding a new level, then the last sum would be the answer we are looking for.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 | /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: int deepestLeavesSum(TreeNode* root) { if (!root) return 0; queue<TreeNode*> Q; Q.push(root); int sum; while (!Q.empty()) { sum = 0; // reset the sum for a new level int curSize = Q.size(); for (int i = 0; i < curSize; ++ i) { auto p = Q.front(); sum += p->val; Q.pop(); if (p->left) { Q.push(p->left); } if (p->right) { Q.push(p->right); } } } return sum; } }; |
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int deepestLeavesSum(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return 0;
queue<TreeNode*> Q;
Q.push(root);
int sum;
while (!Q.empty()) {
sum = 0; // reset the sum for a new level
int curSize = Q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < curSize; ++ i) {
auto p = Q.front();
sum += p->val;
Q.pop();
if (p->left) {
Q.push(p->left);
}
if (p->right) {
Q.push(p->right);
}
}
}
return sum;
}
};The time complexity is O(N) and the space requirement is also O(N) where N is the number of the nodes in the binary tree.
How to Compute the Deepest Leaves Sum of a Binary Tree using Depth First Search Algorithms
We can store the node values in a hash map either unordered_map or map where the key is the depth and the value is the vector of the values. At the same time, we keep track of the maximum depth we’ve visited.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 | /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: int deepestLeavesSum(TreeNode* root) { helper(root, 0); int sum = 0; for (const auto &n: data[curMax]) { sum += n; } return sum; } private: unordered_map<int, vector<int>> data; int curMax = -1; void helper(TreeNode* root, int depth) { if (root == nullptr) return; curMax = max(curMax, depth); data[depth].push_back(root->val); helper(root->left, depth + 1); helper(root->right, depth + 1); } }; |
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int deepestLeavesSum(TreeNode* root) {
helper(root, 0);
int sum = 0;
for (const auto &n: data[curMax]) {
sum += n;
}
return sum;
}
private:
unordered_map<int, vector<int>> data;
int curMax = -1;
void helper(TreeNode* root, int depth) {
if (root == nullptr) return;
curMax = max(curMax, depth);
data[depth].push_back(root->val);
helper(root->left, depth + 1);
helper(root->right, depth + 1);
}
};The C++ map sorts the keys by default, meaning that we can use the rbegin() or –end() to get the maximum key for the map. This simplifies the implementation.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 | /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: int deepestLeavesSum(TreeNode* root) { helper(root, 0); int sum = 0; for (const auto &n: data.rbegin()->second) { sum += n; } return sum; } private: map<int, vector<int>> data; void helper(TreeNode* root, int depth) { if (root == nullptr) return; data[depth].push_back(root->val); helper(root->left, depth + 1); helper(root->right, depth + 1); } }; |
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int deepestLeavesSum(TreeNode* root) {
helper(root, 0);
int sum = 0;
for (const auto &n: data.rbegin()->second) {
sum += n;
}
return sum;
}
private:
map<int, vector<int>> data;
void helper(TreeNode* root, int depth) {
if (root == nullptr) return;
data[depth].push_back(root->val);
helper(root->left, depth + 1);
helper(root->right, depth + 1);
}
};The above DFS implementations have O(N) space requirement (usage of std::map or std::unordered_map), and O(N) time where N is the number of nodes to visit.
Another solution would be to compute the depth of the binary tree first, then compute the sum only for the maximum depth. Both DFS are implemented in Recursion. The sum will be accumulated only when we reach the depth. N nodes will be visited twice.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 | /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: int deepestLeavesSum(TreeNode* root) { if (!root) return 0; int depth = getDepth(root); return getSumAt(root, depth); } private: int getDepth(TreeNode* root) { if (root == NULL) return 0; return max(getDepth(root->left), getDepth(root->right)) + 1; } int getSumAt(TreeNode* root, int depth) { if (root == NULL) return 0; if (depth == 1) return root->val; return getSumAt(root->left, depth - 1) + getSumAt(root->right, depth - 1); } }; |
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int deepestLeavesSum(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return 0;
int depth = getDepth(root);
return getSumAt(root, depth);
}
private:
int getDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
return max(getDepth(root->left), getDepth(root->right)) + 1;
}
int getSumAt(TreeNode* root, int depth) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
if (depth == 1) return root->val;
return getSumAt(root->left, depth - 1) +
getSumAt(root->right, depth - 1);
}
};–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
推荐阅读:红梅本来有几粒糖 摸黄球白球可能性的问题 如果要准时到达需要多少小时 货物的原价是多少元 用去水泥和沙子各多少吨 求AB两站距离的问题 如图小正方形的边长为5cm求阴影部分的面积 全天计划生产消毒药水多少瓶 等候上菜和用餐的时间总和最少是多少 在一次环保知识竞赛中
- 评论列表
-
- 添加评论