How many different ways can £2 be made using any number of coins
- 时间:2020-09-10 12:45:51
- 分类:网络文摘
- 阅读:136 次
In the United Kingdom the currency is made up of pound (£) and pence (p). There are eight coins in general circulation:
1p, 2p, 5p, 10p, 20p, 50p, £1 (100p), and £2 (200p).
It is possible to make £2 in the following way:
1×£1 + 1×50p + 2×20p + 1×5p + 1×2p + 3×1pHow many different ways can £2 be made using any number of coins?
Depth First Search Algorithm
Let’s define a function f takes two parameters (amount and last). Thus, we can perform a Depth First Search (DFS) search based on the following
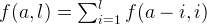
The f(0, x) is 1. We avoid duplicate solution by limiting the current coin strictly less or equal than the last coin.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | function dfs(amount, last) { if (amount === 0) return 1; const coins = [1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 200]; let ans = 0; for (let x of coins) { // iterate over the coins if (amount- x >= 0 && x <= last) { // non-bigger ans += dfs(amount - x, x); // recursive dfs } } return ans; } console.log(dfs(200, 200)); |
function dfs(amount, last) {
if (amount === 0) return 1;
const coins = [1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 200];
let ans = 0;
for (let x of coins) { // iterate over the coins
if (amount- x >= 0 && x <= last) { // non-bigger
ans += dfs(amount - x, x); // recursive dfs
}
}
return ans;
}
console.log(dfs(200, 200));The answer is 73682. We can also place a non-less coin and we need to call initially with last equal to 0:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | function dfs(amount, last) { if (amount === 0) return 1; const coins = [1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 200]; let ans = 0; for (let x of coins) { // iterate over the coins if (amount- x >= 0 && x >= last) { // non-smaller ans += dfs(amount - x, x); // recursive dfs } } return ans; } console.log(dfs(200, 0)); |
function dfs(amount, last) {
if (amount === 0) return 1;
const coins = [1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 200];
let ans = 0;
for (let x of coins) { // iterate over the coins
if (amount- x >= 0 && x >= last) { // non-smaller
ans += dfs(amount - x, x); // recursive dfs
}
}
return ans;
}
console.log(dfs(200, 0));Counting Number of Coins using Dynamic Programming Algorithm
We notice that we can save the intermediate results so that we don’t respawn too many recursions. The easiest way is to pass a dictionary (or hash map) as a last parameter.
The following Javascript code implements the Dynamic Programming Algorithm to count the coins based on the Recursive Depth First Search with Memoization Technique.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | function dfs(amount, last, cached = {}) { if (amount === 0) return 1; const coins = [1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 200]; // if it has been calculated, then return it if (typeof cached[amount + "-" + last] !== "undefined") { return cached[amount+ "-" + last]; } let ans = 0; for (let x of coins) { if (amount - x >= 0 && x >= last) { ans += dfs(amount- x, x, cached); } } // save the result in the memo cached[amount+ "-" + last] = ans; return ans; } console.log(dfs(200, 0)); |
function dfs(amount, last, cached = {}) {
if (amount === 0) return 1;
const coins = [1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 200];
// if it has been calculated, then return it
if (typeof cached[amount + "-" + last] !== "undefined") {
return cached[amount+ "-" + last];
}
let ans = 0;
for (let x of coins) {
if (amount - x >= 0 && x >= last) {
ans += dfs(amount- x, x, cached);
}
}
// save the result in the memo
cached[amount+ "-" + last] = ans;
return ans;
}
console.log(dfs(200, 0));We can slightly rewrite this, using iterative approach. We sort the coins and start from the smallest coin. For each coin, we then incrementally update the answer.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | function dp(amount) { let f = Array(amount + 1).fill(0); f[0] = 1; for (let x of [1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 200]) { for (let a = x; a <= amount; ++ a) { f[a] += f[a - x]; } } return f[amount]; } |
function dp(amount) {
let f = Array(amount + 1).fill(0);
f[0] = 1;
for (let x of [1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 200]) {
for (let a = x; a <= amount; ++ a) {
f[a] += f[a - x];
}
}
return f[amount];
}The algorithmic complexity is O(NM) where N is the number of the coin-types and M is the amount. The space complexity is O(M).
–EOF (The Ultimate Computing & Technology Blog) —
推荐阅读:推荐5大养胃食物帮助呵护你的“胃” 红薯营养丰富但空腹吃红薯需要谨慎 香蕉不能和哪些食物一起食用呢? 男性多吃香蕉有助于性功能疾病的康复 权威发布:常见的致癌食物你吃过几种 “最大份扬州炒饭”喂猪背后的浮躁心态 吉尼斯宣布“最大份扬州炒饭”纪录无效 包菜有意想不到的防癌养胃保健功效 食药总局公布不合格食品名单蜂蜜上黑榜 板栗养胃健脾是医药学家推崇的补肾果
- 评论列表
-
- 添加评论